Introduction
The 2024 Global Electricity Review by Ember presents research that highlights the profound impact of the renewable energy sector on the global electricity landscape. For the first time, renewables have reached the milestone of generating 30% of the world's electricity, driven largely by significant advances in solar and wind technologies.
The expansion of renewable energy is redefining existing job descriptions and creating entirely new opportunities as the electricity generation industry adapts to more sustainable practices.
This article aims to explore the implications of Ember's findings, focusing on how the evolving power generation landscape could affect career paths, skill requirements and employment opportunities.
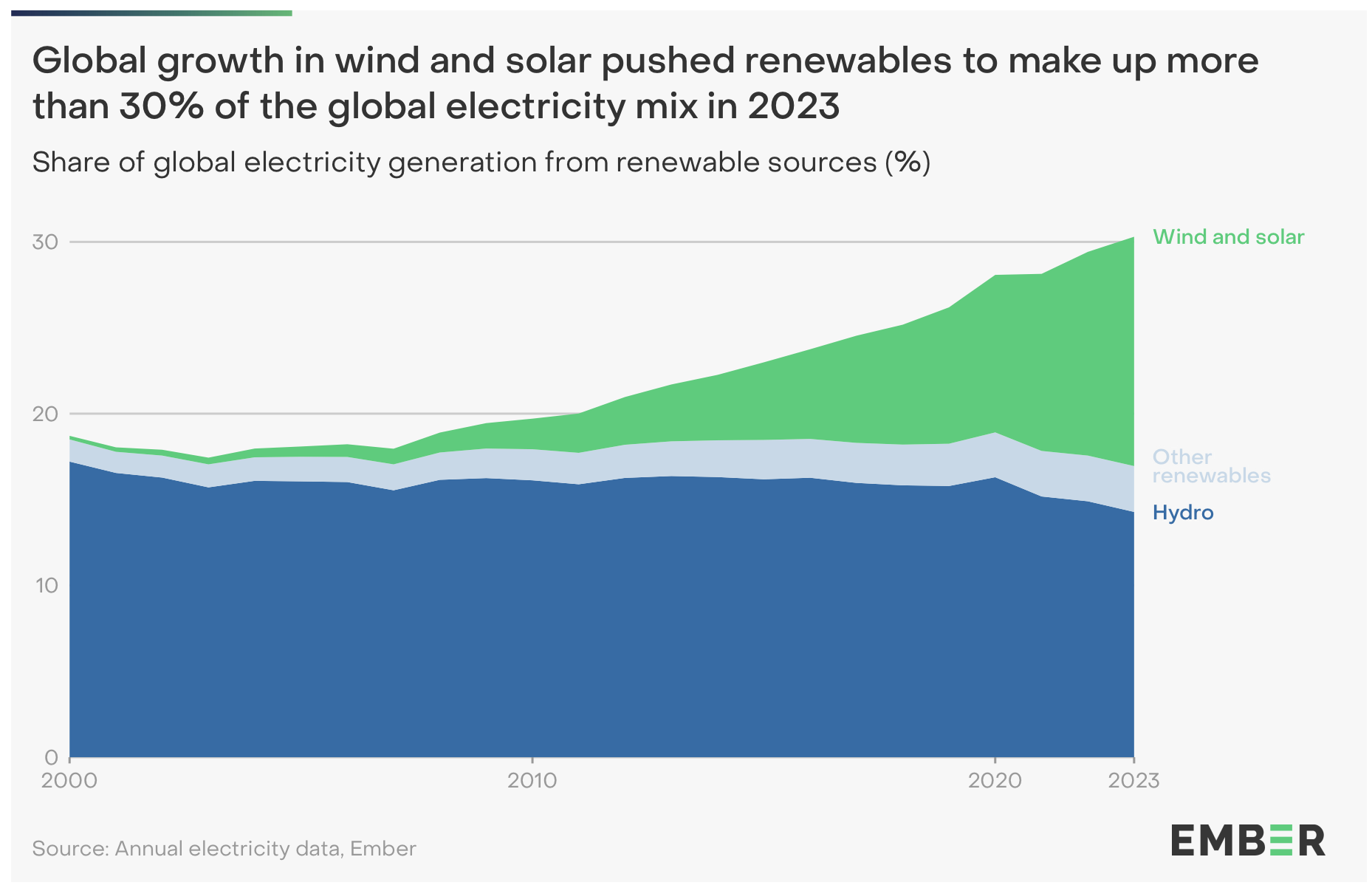
Figure 1 - Share of global electricity generation from renewable source (%) between 2000 — 2023
The Rise of Renewables in Global Electricity Generation
Record Contributions from Solar and Wind
The growth in renewable energy's contribution to global electricity in 2023 has been driven by solar and wind power, which are now at the forefront of the energy sector's transformation. Solar, in particular, grew faster than any other energy source for the 19th consecutive year. In 2023, solar installations exceeded those of any other energy source, surpassed wind to become the largest source of new electricity for the second year running 1.
This rapid expansion of solar and wind energy has a direct positive impact on the Earth's atmosphere as well as the creation of jobs around the world. As more solar panels and wind turbines are installed, the demand for skilled professionals to design, manufacture, install and maintain these systems continues to grow.
Demand for Electricity Drives Jobs Creation
Growth in Electricity Demand
2023 marked another record year for electricity demand, which increased by 627 TWh, the equivalent of adding all of Canada's electricity consumption to the global grid.
This increase, while slightly below the average growth of recent years, was largely driven by the rapid adoption of new technologies such as electric vehicles (EVs), heat pumps, electrolysers, air conditioning and data centres 1.
Job Creation in Emerging Tech Sectors
As demand for electricity grows, so does the need for innovative solutions. The expansion of electric vehicles, heat pumps, renewable energy integration and smart infrastructure development is creating new opportunities in the value chain and associated services. For example, the EV market is also creating jobs in battery manufacturing, charging infrastructure, network management systems and AI development.
Similarly, the massive energy requirements of data centres lead to a surge in new positions related to renewable energy sourcing, energy management systems and sustainability consulting. These roles are critical as organisations seek to reduce their environmental impact while managing growing energy demands. They represent a new range of opportunities for electrical engineers, IT specialists and environmental policy experts.
And while we often think of technical roles when we talk about energy, it’s also marketers, managers, programmers, legal and all sorts of other people who are needed to keep the momentum of the renewable energy revolution going.
Declining Fossil Generation and Increasing Clean Energy
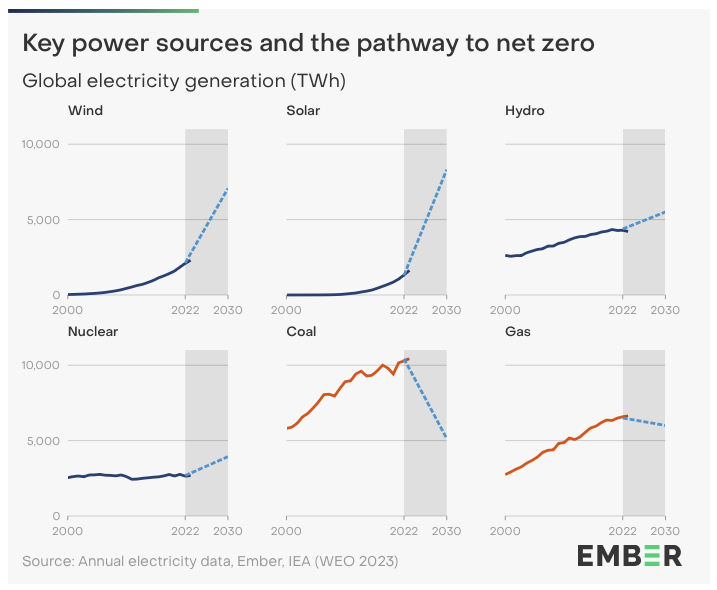
Figure 2 - Global electricity generation (TWh, 2000 — 2030) including a projection meeting the IEA Net Zero pathway
Projections for Fossil and Clean Energy Trends
Looking ahead to 2024 and beyond, Ember's report forecasts a continued decline in fossil fuel generation coupled with a significant increase in clean energy output. This trend is expected to be powered by technological advancements and a global, collective commitment to reduce carbon emissions.
The decline in fossil fuel use is anticipated to reduce job opportunities in traditional coal, oil, and gas industries. But this contraction is more than offset by the expansion in renewable sectors, particularly in solar and wind energy. The expertise of current fossil fuel industry employees is of course required in the clean energy transition, as much of the skill sets overlap, and certain expertise is predominantly found in the fossil fuels industry. For instance offshore engineering: same cool job, just sustainable.
Conclusion
The transition to renewable energy is a necessity for climate change mitigation. And as the Ember GER 2024 shows, the transition is well underway.
The concentration of carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere has grown by 50% since people started burning fossil fuels back in the 19th century, and it continues growing faster than ever, dangerously pushing the Earth further off its balance day after day.
We better get to work and make use of the technologies that we already know how to manufacture, deploy and optimise, technologies that are mature, effective, and scalable, and directly affect how much less carbon we add to the atmosphere every day.
1 Wiatros-Motyka, M., Fulghum, N., Jones, D. et al. (2024) ‘Global Electricity Review 2024’, Ember. Available at: https://ember-climate.org/insights/research/global-electricity-review-2024/.
Article by Jaroslav Holub
Published on May 09, 2024
Share this article with your folks, and help them find a career to be proud of.



